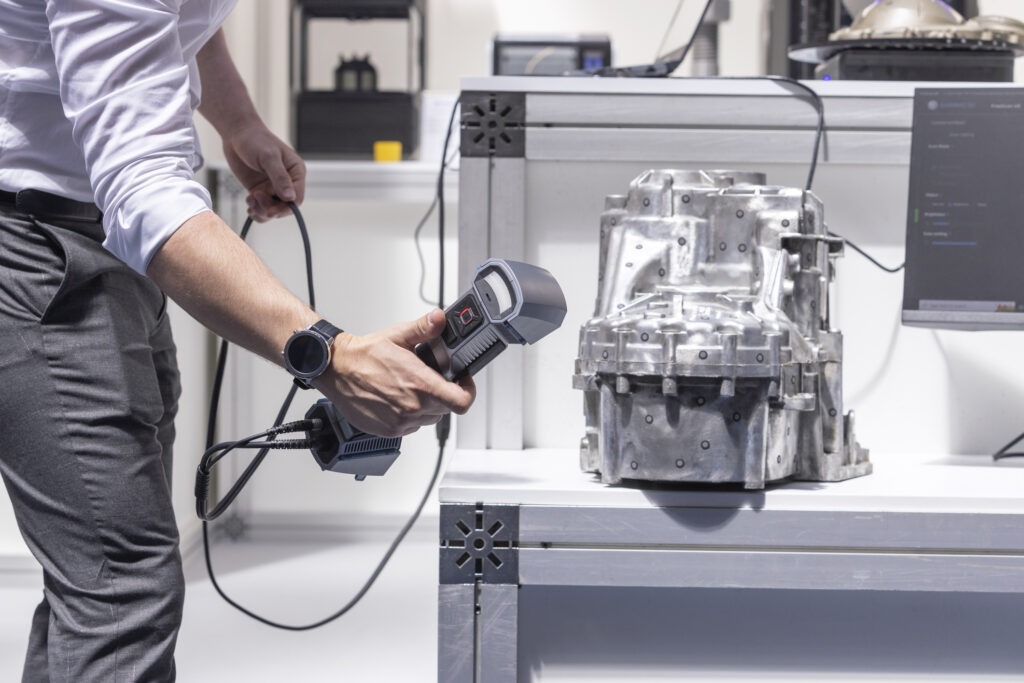
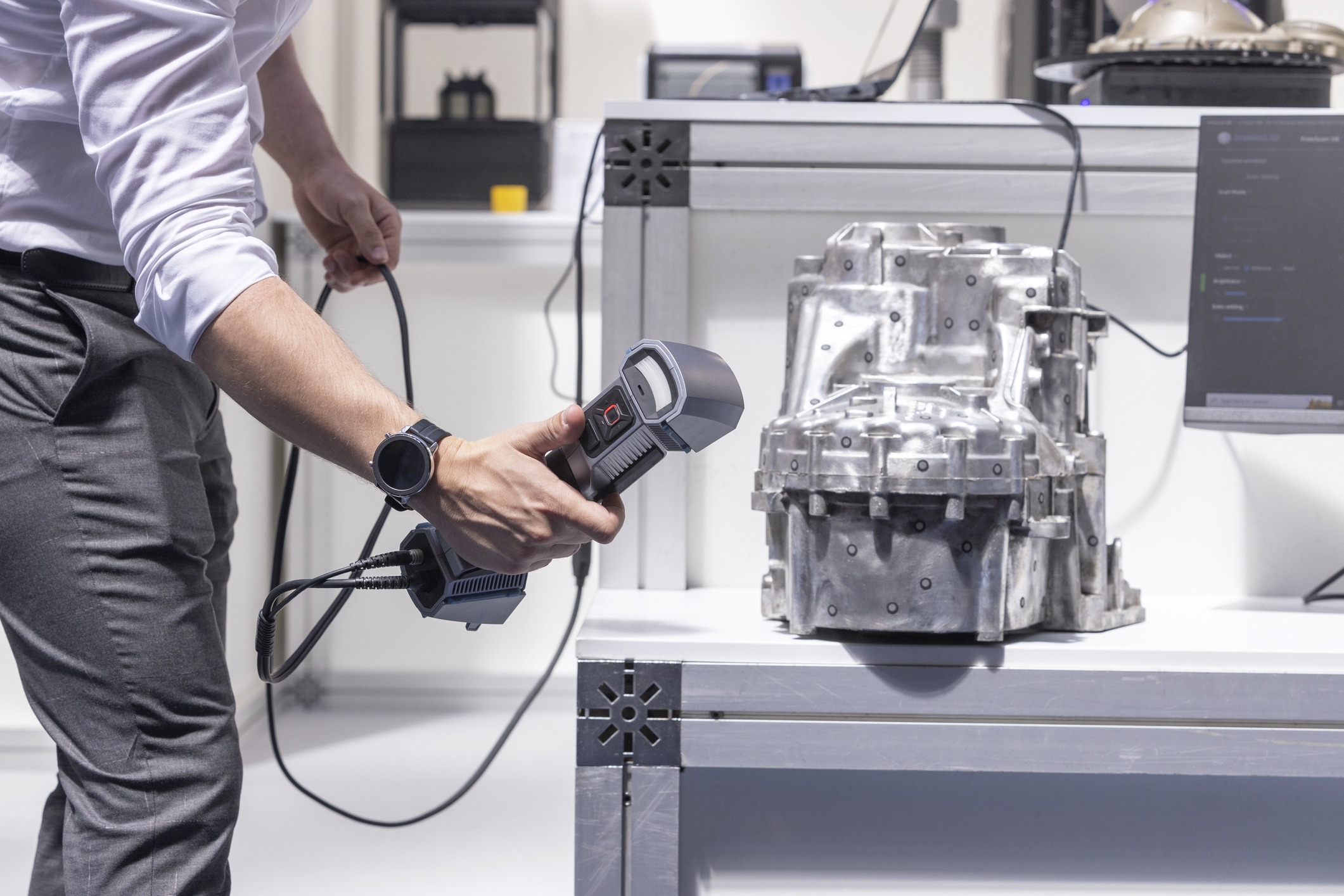
What is the difference between 3D laser scanning vs photogrammetry? What is the best digitizing method for your project?
As technology continues to advance, there are now more options than ever for collecting data. Two popular methods for capturing 3D data are 3D laser scanning and photogrammetry.
Both methods have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, but ultimately the choice between 3D laser scanning vs photogrammetry, will depend on the specific project requirements.
In this article, we will explore the differences between 3D laser scanning vs photogrammetry, and highlight their pros and cons.
What is 3D Laser Scanning?
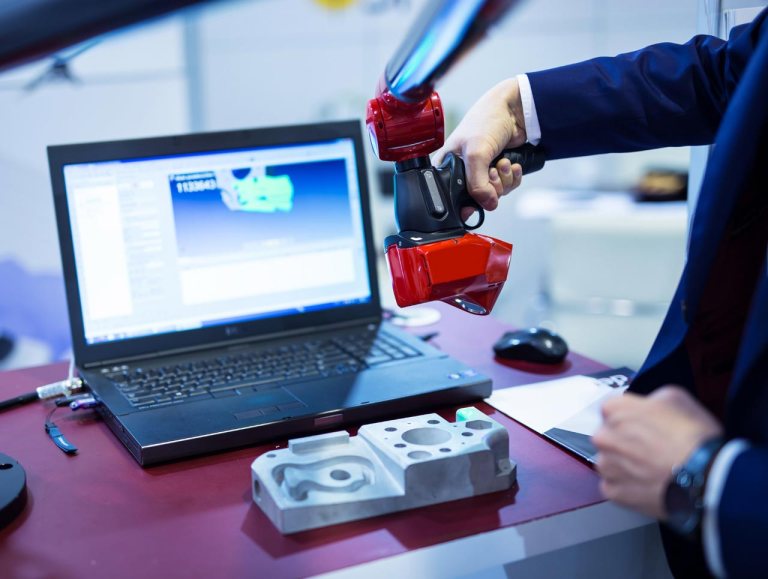
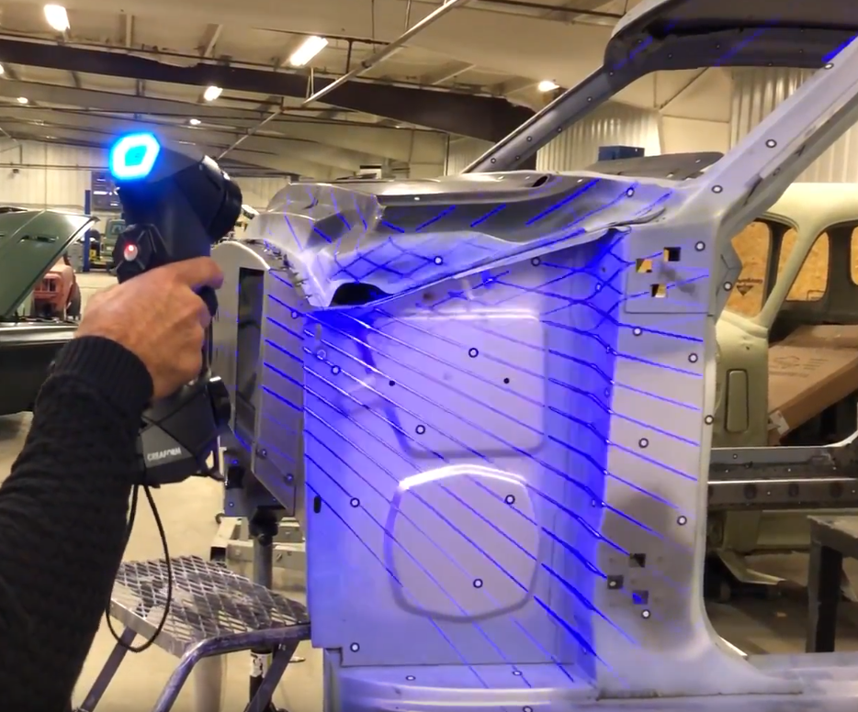
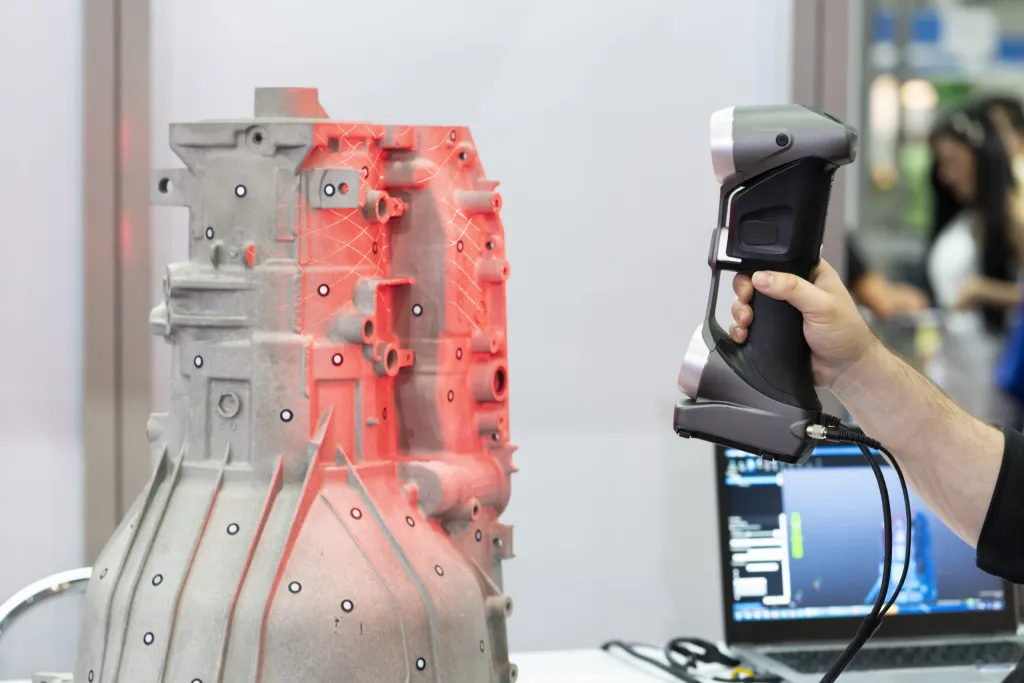
3D laser scanning is a technology that uses a laser to capture a point cloud of an object or scene. The laser emits a beam of light that bounces off the object and returns to the scanner, which measures the time it took for the light to travel and calculates the distance to the object.
This process is called triangulation.
Multiple scans are taken from different angles and combined to create a complete 3D model of the object or scene. The resulting point cloud is a collection of millions of points in 3D space, each with its own X, Y, and Z coordinates.
What is Photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry is a process that uses photographs to create 3D models of objects or scenes. Multiple photographs are taken from different angles and then processed using specialized software that can triangulate the position of each point in 3D space.
The resulting 3D model is a mesh made up of thousands or even millions of photos, each with its own texture and color information.
Some of the most powerful photogrammetry results come from stepping into a room with hundreds of cameras. The project is set in the middle and all of the cameras go off in unison, capturing 360 degrees of the project and piecing together each photo.
Advantages of 3D Laser Scanning vs Photogrammetry
One of the biggest advantages of 3D laser scanning is its speed and accuracy. A laser scanner can capture millions of points in just a few minutes, and the resulting point cloud is incredibly accurate – typically within a few millimeters of the actual object.
This makes 3D laser scanning ideal for capturing detailed information about complex objects or structures, such as buildings, bridges, and industrial machinery. It can also be used for capturing topographical data, such as the contours of a landscape or the shape of a riverbed.
For reverse engineering purposes, laser scanners are able to detect the smallest detail to the thousandths of a millimeter. By digitizing an existing surface, 3D laser scanning speeds up CAD file creation of the scan data meshes.
Read about the 5 Advantages of 3D laser Scanning for Reverse Engineering.
Another advantage of 3D laser scanning is its ability to capture data in various environments. Sunlight and color do not affect the scan data as much as in photogrammetry. Since a series of lasers are used, 3D scanning services can be performed in almost any condition.
and color do not affect the scan data as much as in photogrammetry. Since a series of lasers are used, 3D scanning services can be performed in almost any condition.
This makes it ideal for use in environments where traditional photography would be difficult or impossible, such as dark workshops or in the daylight.
Disadvantages of 3D Laser Scanning
The biggest disadvantage of 3D laser scanning is its cost. Due to the high level of accuracy, laser scanners are expensive pieces of equipment, and the cost of the scanner itself is just the beginning. It also requires specialized software and skilled technicians to operate and process the data.
Instead of investing into a 3D laser scanning platform, many will reach out to 3D scanning service providers.
Interested in service provider? Read up on How to Find the Best 3D Scanning Services Near Me.
Another disadvantage of 3D laser scanning is its limited range. Laser scanners are restricted to its connection to a power source. It may not be suitable for capturing data over larger areas but what you gain in scanning a large area, you lose in accuracy.
Advantages of Photogrammetry
One of the biggest advantages of photogrammetry is its low cost. All that is needed is a camera and specialized software, both of which are relatively inexpensive.

Another advantage of photogrammetry is its flexibility. It can be used to capture data from a wide range of objects and scenes, from small objects like people, toys or jewelry to large structures like buildings and bridges.
Finally, photogrammetry is ideal for capturing data over large areas. With a drone or aircraft, it is possible to capture data over hundreds or even thousands of hectares in a single flight.
Disadvantages of Photogrammetry
One of the biggest disadvantages of photogrammetry is its accuracy. While photogrammetry can produce high-quality 3D models, the accuracy is not as good as 3D laser scanning. This is because photogrammetry relies on stitching together thousands of photos and assumes that the camera positions and orientations are known.
Another disadvantage of photogrammetry is its dependence on good lighting conditions. If the lighting is poor, it can be difficult to capture high-quality images, which can result in lower accuracy and resolution of the resulting 3D model.
Additionally, photogrammetry can be affected by motion blur, lens distortion, and other image artifacts. These can be mitigated through careful camera calibration and image processing, but it can add to the overall time and effort required for the project.
In quick comparison, 3D laser scanners are not affected by shiny projects whereas photogrammetry would struggle. But, a 3D laser scanner can not record objects that move, even slightly, so it is not advantageous to use for scanning a person .
3D Laser Scanning vs Photogrammetry: Which is Right for Your Project?
Both 3D laser scanning and photogrammetry have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two will depend on the specific needs of the project.
For projects that require high accuracy and detailed data, such manufacturing components, quality control inspections, or CAD file creation, 3D laser scanning will be the best option. 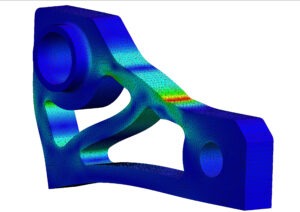
It can capture millions of points with high accuracy, even in low-light conditions, and can produce detailed 3D models that can be used for analysis and visualization.
For projects capturing data over large areas or for people, photogrammetry will be the better choice. It is a more cost-effective solution that can capture data from a range of objects and scenes, and can cover larger areas in a shorter amount of time.
It is worth noting that both technologies can be used in combination to produce more complete and accurate 3D models. For example, laser scanning can be used to capture the detailed geometry of a building, while photogrammetry can be used to capture the textures and colors of the building’s surfaces.
Conclusion
When comparing 3D laser scanning vs photogrammetry, both are valuable tools for capturing existing surfaces. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice between the two will depend on the needs of your project.
While 3D laser scanning is more accurate and suitable for capturing detailed data from complex objects or structures, it may not be suitable for capturing data over large areas.
On the other hand, photogrammetry is ideal for capturing data from a range of objects and scenes, but it will not be as accurate as laser scanning.
Ultimately, the choice between the two technologies will depend on a variety of factors, including project requirements, budget, and timelines.
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of 3D laser scanning vs photogrammetry, allows you to make informed decisions about which technology is best suited for your project.