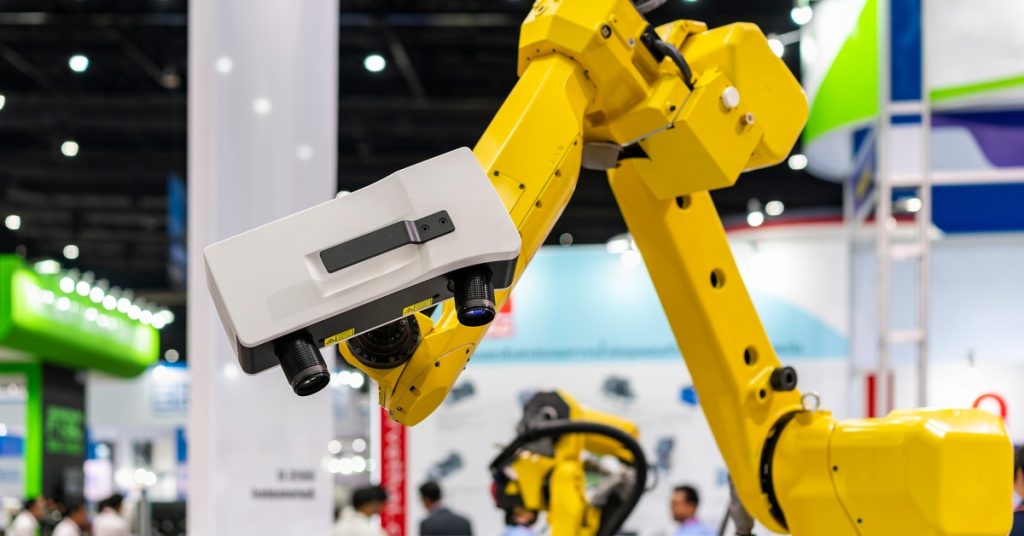
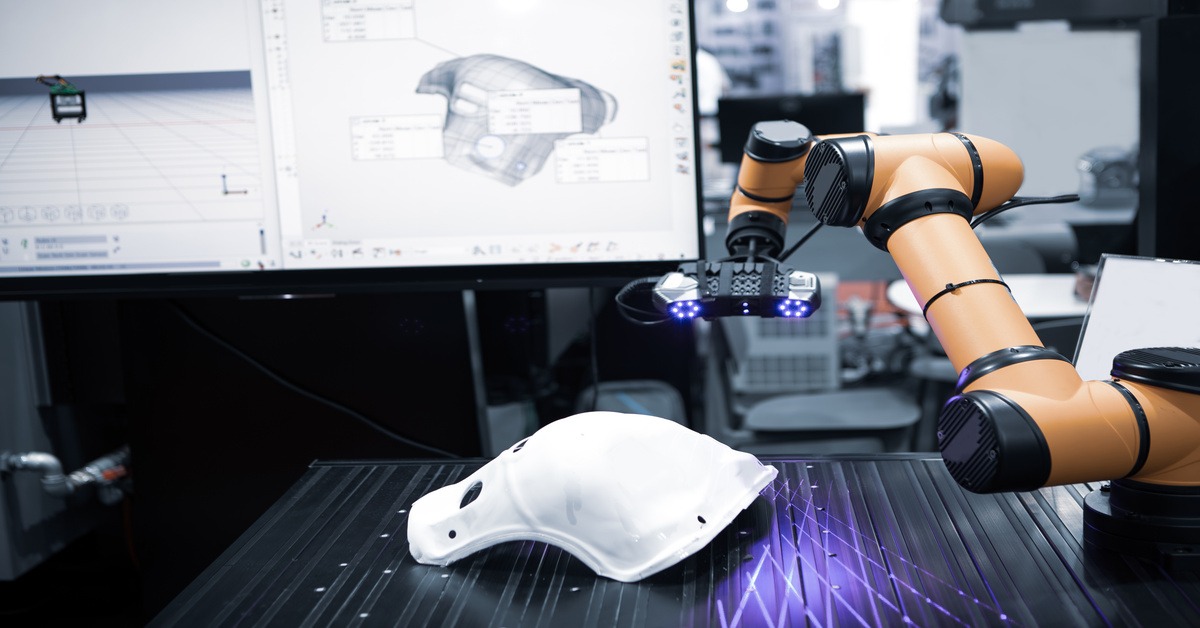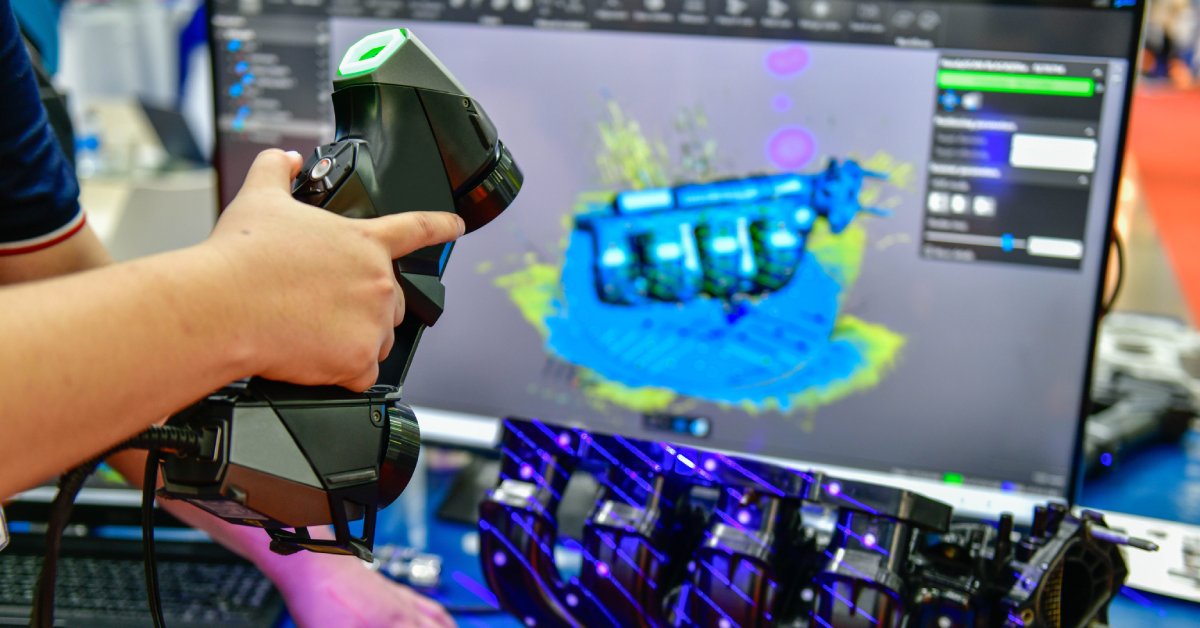
3D laser scanning technology captures the precise shape of physical objects using laser light to create dense point clouds or polygon meshes. These “digital twins” of real-world objects and environments are incredibly accurate and detailed.
As this technology has become more accessible and powerful, its importance has grown exponentially. Organizations across numerous sectors now rely on it to improve accuracy, speed up processes, and unlock new possibilities. This guide will explore ten key industries that commonly use 3D laser scanning, highlighting the specific applications and benefits that make this technology so transformative.
Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC)
In the AEC industry, precision is everything. 3D laser scanning provides the high-fidelity data needed to plan, design, and execute projects with confidence. Teams use it to create highly accurate 3D models for Building Information Modeling (BIM), which serves as a central database for the entire project lifecycle. Scanners quickly capture site conditions for pre-construction surveys, ensuring that designs are based on real-world data.
For renovation and restoration projects, especially on historical buildings, laser scanners document intricate details without physical contact, preserving the structure’s integrity while providing a precise blueprint for the work ahead. This leads to improved accuracy, fewer construction errors, and significantly faster project timelines.
Manufacturing and Industrial Design
Manufacturing relies on tight tolerances and efficient workflows, making laser scanning services invaluable to them. One of the primary applications of this type of service is reverse engineering. This is where manufacturers scan an existing part to create a digital model for analysis, modification, or reproduction. This is particularly useful when original design files are lost or when analyzing a competitor’s product.
Scanners are also crucial for quality control, allowing for detailed inspection of parts against their CAD models to identify defects or deviations. By integrating this technology, manufacturers can streamline production processes, enhance precision in product design, and achieve significant cost savings through more efficient workflows.
Automotive and Aerospace

The automotive and aerospace industries operate under stringent safety and performance standards. 3D laser scanning helps meet these demands by enabling the precise design and testing of components. From engine parts to fuselage sections, scanning ensures every piece fits and functions perfectly. In Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) operations for aircraft, scanners are used to inspect for damage and wear, creating accurate models for repair work.
This tech is also helpful in crash analysis, where teams can scan a vehicle or accident scene to reconstruct the event and gather data for safety improvements. The result is improved safety, better performance, and faster innovation cycles for new vehicles and aircraft.
Oil and Gas
The oil and gas industry involves massive, complex infrastructure where safety and reliability are paramount. That means these companies need to hire groups that can perform massive 3D laser scans to map and model pipelines, refineries, and offshore platforms with incredible detail. This allows engineers to monitor structural integrity, check for wear, and plan complex installations or retrofits without disrupting operations.
The highly accurate as-built documentation helps ensure compliance with strict industry regulations. By using this technology, companies can enhance worker safety, reduce costly downtime during maintenance, and manage their assets more effectively.
Healthcare and Medical Devices
In healthcare, 3D laser scanning is driving a new era of personalized medicine. Medical professionals utilize this tech to create custom-fit prosthetics and orthotics, scanning a patient’s limb to design a device that is both comfortable and functional. Surgeons also use scanned data to plan complex procedures, creating 3D models of a patient’s anatomy to simulate the operation beforehand, which leads to much better outcomes.
Additionally, the technology is essential for the quality control and manufacturing of intricate medical devices, ensuring they meet exact specifications. These applications directly contribute to personalized patient care and improved results in medical procedures.
Entertainment and Media
From blockbuster movies to immersive video games, 3D laser scanning is transforming how people create digital content. For eample, artists and designers use scanners to create highly realistic 3D models of actors, props, and entire environments. They then use this digital data to build virtual worlds and generate stunning visual effects.
The technology powers virtual and augmented reality experiences as well by capturing real-world spaces for users to explore digitally. People have even found ways to use this tech to aid in the digital preservation of movie sets and props, creating an archive for future use. This leads to enhanced visual effects, more compelling storytelling, and more cost-effective production processes.
Forensics and Law Enforcement
For investigators, accuracy is non-negotiable. 3D laser scanners have become critical tools in modern forensics for their ability to capture crime scenes with objective detail. The technology creates a permanent, tamper-proof 3D record of the scene, documenting the exact position of evidence without disturbing it.
Police can then use this data for crime scene reconstruction, accident investigation, and creating compelling 3D visuals for courtroom presentations. The level of detail and accuracy provided by laser scanning improves evidence collection and helps build stronger, more persuasive cases.
Real Estate and Property Management
In real estate, giving potential buyers a comprehensive view of a property is key to closing a sale. That’s why these companies have started using services that provide 3D laser scanning to create immersive virtual tours that let people explore a home from anywhere in the world.
Architects and interior designers also use scans for space planning, ensuring furniture and new layouts will fit perfectly. For property managers, scanning provides precise documentation of as-built conditions, which is helpful for maintenance, renovations, and facility management. The potential uses for this kind of technology are nearly limitless in this industry.
Environmental and Geospatial Studies
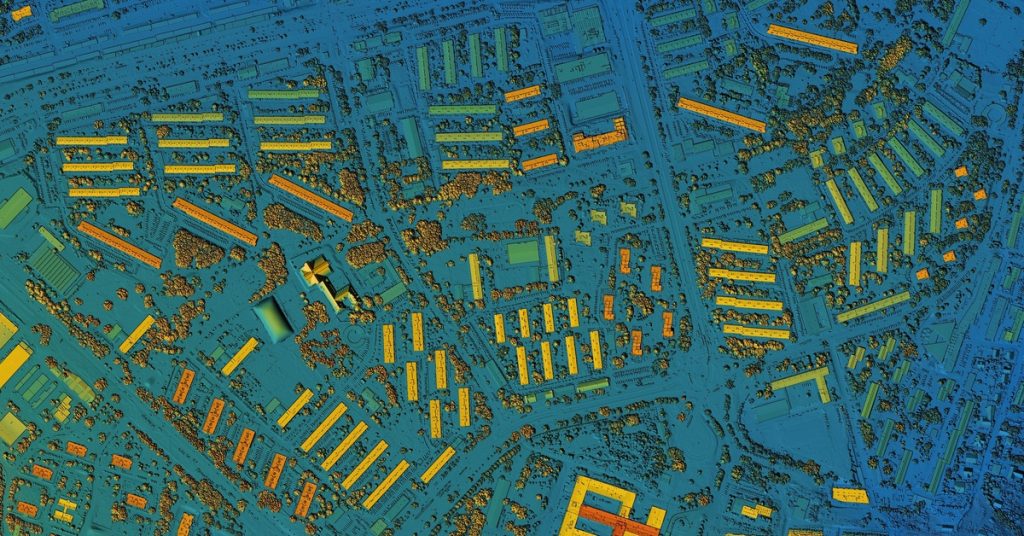
Understanding our planet requires accurate data on a massive scale. 3D laser scanning, often deployed via aerial platforms (LiDAR), is used to map vast terrains and landscapes for environmental and geospatial studies. Scientists use it to monitor coastal erosion, track changes in forest biomass, and assess the impact of natural disasters.
In urban planning, scans provide the detailed data needed to design infrastructure and model city growth. The information gathered supports better decision-making for sustainability initiatives and provides an accurate foundation for large-scale development projects.
Marine and Shipbuilding
Building and maintaining ships is a complex engineering feat. That’s why the marine industry is among the most common to use 3D laser scanning. Most notably, it aids in the design and retrofitting of vessels by providing precise as-built data of existing structures. Shipbuilders use scanners to inspect hulls and other components for deformities or damage, both during construction and as part of ongoing maintenance.
Teams can also apply the technology to their inspection process of offshore platforms and underwater structures, ensuring their integrity in harsh marine environments. The benefits include improved safety, greater efficiency in the shipyard, and reduced costs in both shipbuilding and repair operations.






