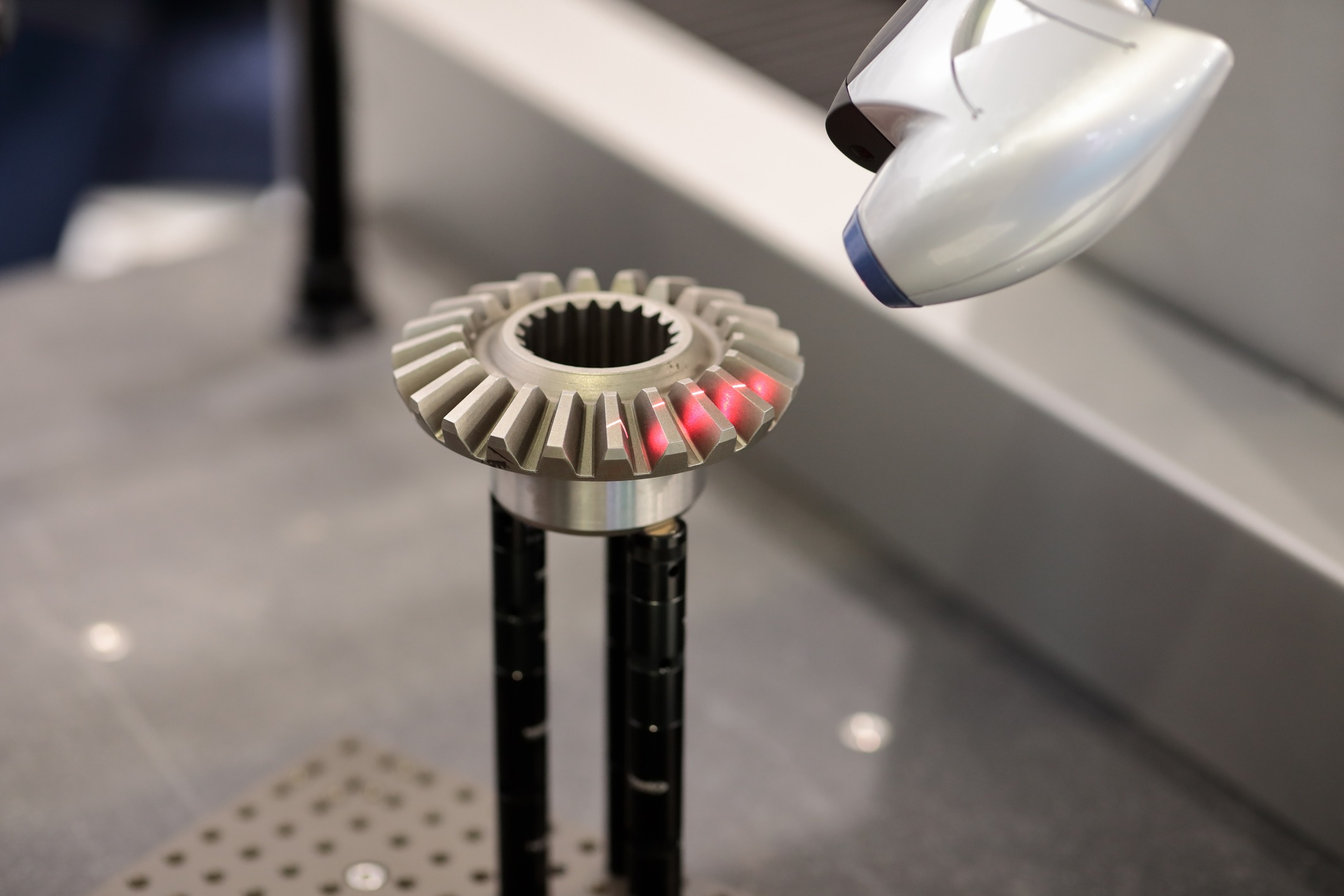
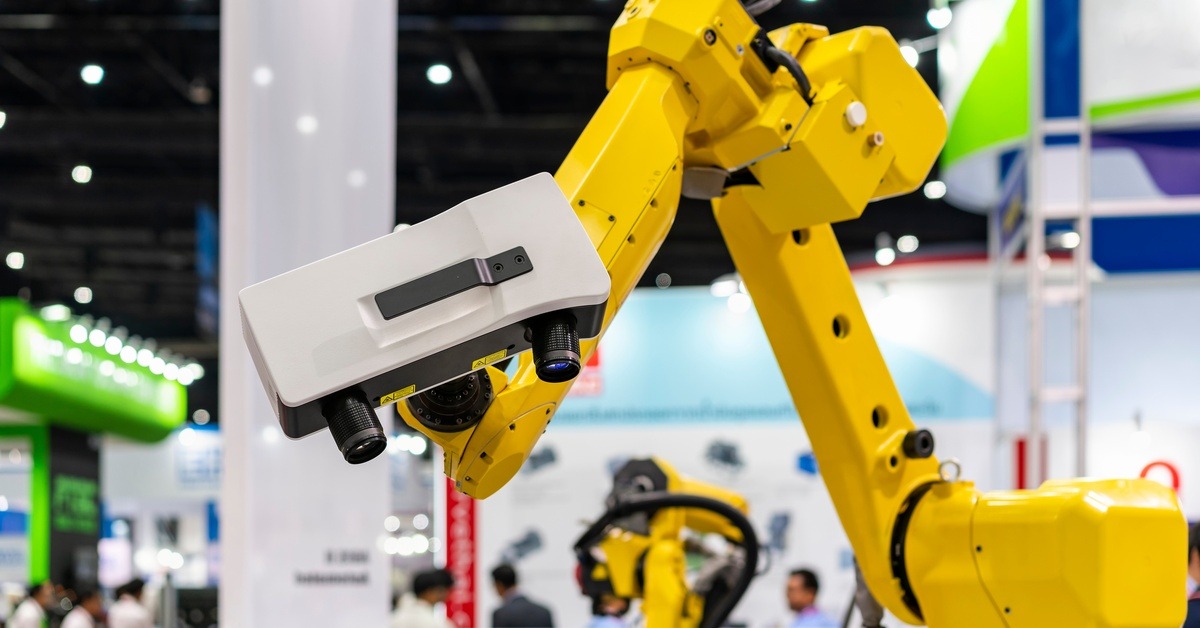
3D laser scanning has become one of the most valuable tools in modern engineering. Whether you’re designing parts, validating tolerances, reverse engineering legacy components, or capturing complex geometry that would be impossible to measure manually, laser scanning delivers speed, accuracy, and repeatability that traditional measurement can’t match.
But what exactly is 3D laser scanning? How does it work? What industries benefit from it? And why has it become essential for companies working in manufacturing, aerospace, motorsports, automotive, consumer products, and defense?
This complete beginner friendly, yet engineer-focused, guide breaks down everything you need to know.
What Is 3D Laser Scanning?
3D laser scanning is a non-contact measurement technology that captures the exact geometry of a physical object or environment. It does this by projecting laser lines or patterns onto a surface, recording millions of points per second, and converting them into a high-resolution 3D model known as a point cloud or mesh.
The result is a precise, digital “twin” of the object, including all contours, curvature, holes, edges, and surface details — all captured far more accurately than manual measurement tools such as calipers, CMM arms, or tape measures.
At Tangent Solutions, we use metrology-grade 3D laser scanners capable of achieving 0.025–0.035 mm accuracy, making them suitable for demanding engineering applications.
How 3D Laser Scanning Works
Although many scanner types exist, the core process follows three steps:
1. Data Capture (Laser Projection & Sampling)
A handheld or tripod-mounted scanner projects laser lines onto the object. As the scanner moves around the part, sensors record how the laser lines deform and reflect, allowing the system to calculate distance, curvature, and surface position.
2. Point Cloud Generation
Millions of individual measurements — called data points — are captured each second. These points create a dense, highly accurate “cloud” that represents the object in 3D space.
3. Mesh Cleanup & CAD Conversion
After the scan, engineers clean and align the data before turning it into a usable digital format, such as:
-
Mesh files (STL, OBJ, PLY)
-
Parametric CAD models (STEP, IGES, XT)
-
NURBS surfaces
-
Inspection reports (GD&T, deviation maps)
For many clients, Tangent Solutions also handles full reverse engineering, where we convert raw scan data into editable, manufacturable CAD geometry.
What Can 3D Laser Scanning Capture?
Laser scanning works on nearly any object, including:
-
Mechanical parts
-
Tools & fixtures
-
Aerospace components
-
Automotive and motorsports assemblies
-
Industrial machinery
-
Plastics, castings, stampings
-
Architectural spaces
-
Aftermarket parts
-
Consumer products
-
Molded, organic, or irregular shapes
It excels on complex surfaces that would be tedious — or impossible — to measure manually.
Why 3D Laser Scanning Matters in Engineering
3D scanning isn’t just “nice to have.” It has become mission-critical across engineering disciplines for speed, precision, and design accuracy.
Here’s why:
1. Metrology-Level Accuracy
Laser scanners capture millions of points per second with extremely tight tolerances. This ensures dimensional accuracy on par with CMM machines — but with greater speed and mobility.
Engineering teams use this for:
-
Tolerance analysis
-
Fitment validation
-
GD&T inspection
-
Quality assurance
-
Tooling verification
High-accuracy data eliminates guesswork during design or manufacturing.
2. Speed: Reduce Measurement Time From Days to Hours
Traditional measurement methods require hours of manual labor — especially on complex surfaces.
3D laser scanners complete full scans in:
-
30 minutes to 3 hours for most components
-
Same-day delivery for raw mesh or cleaned data
-
1–3 days for CAD-ready deliverables
This accelerated speed helps companies reduce cycle times, prototype faster, and catch issues before they become costly.
3. Ideal for Reverse Engineering
When legacy parts have no drawings, no CAD files, or outdated documentation, 3D scanning becomes the fastest way to recreate them digitally.
This is especially valuable in industries like:
-
Motorsports (custom brackets, intakes, aero components)
-
Aerospace (replacement parts for aging aircraft)
-
Manufacturing (legacy tooling, discontinued components)
-
Automotive R&D (aftermarket fitment, performance upgrades)
Tangent Solutions specializes in scan-to-CAD workflows to produce precise, fully editable 3D models.
4. Perfect for Complex Geometry
Freeform surfaces, curves, castings, and organic shapes are notoriously difficult to measure.
Laser scanning captures:
-
Deep pockets
-
Inside edges
-
Sweeping curves
-
Irregular organic shapes
-
Undercuts
-
Worn or damaged geometry
This ensures the CAD model reflects the part exactly as it physically exists.
5. Excellent for Fitment & Packaging Studies
Before manufacturing expensive prototypes, e-commerce brands can use scan data to digitally evaluate:
-
Assembly fit
-
Interference detection
-
Packaging constraints
-
Spatial clearances
-
Fixture design
-
Mounting alignment
This eliminates redesigns and prevents compatibility issues.
How 3D Laser Scanning Is Used Across Industries
Let’s break down specific, real world applications for the industries Tangent Solutions serves.
Manufacturing & Industrial Engineering
Manufacturers rely on 3D scanning for:
-
Tooling & mold validation
-
Quality control
-
Production part inspection
-
Line improvements & automation integration
-
Reverse engineering worn components
-
Digital archiving of parts
The accuracy and speed of scanning help reduce scrap, shorten production cycles, and optimize manufacturing workflows.
Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace demands the highest precision. 3D laser scanning is used for:
-
Wing, fuselage, or aero surface analysis
-
Repair part validation
-
Airframe inspection
-
Fitment evaluation for new avionics or equipment
-
Reverse engineering components for aging aircraft
-
Composite part verification
Scan data supports engineering teams working under strict quality and regulatory requirements.
Motorsports & Automotive Engineering
Time is everything in motorsports. 3D scanning accelerates design and testing by providing:
-
Chassis and roll cage scanning
-
Aero part design: splitters, wings, diffusers
-
Custom mounting brackets
-
Engine bay scanning for component packaging
-
Aftermarket part development
-
Rapid prototyping verification
Teams can model exact fitment before producing a single physical part.
Defense & Tactical Engineering
Defense applications often include:
-
Weapon system modeling
-
Mount and fixture engineering
-
Vehicle interior/exterior mapping
-
Armor and ballistic component scanning
-
Replacement part reproduction
-
Maintenance and repair operations
Laser scanning supports secure, precise engineering under high-stakes environments.
Consumer Products & R&D
Brands use scanning for:
-
Product redesign
-
Ergonomic studies
-
Plastic injection molded part validation
-
3D printing workflows
-
Prototype refinement
-
Surface modeling and visualization
It reduces development time and improves final product quality.
Types of 3D Scanning Technologies
While “3D laser scanning” is the general term, scanners come in a few categories:
1. Laser Line Scanners
Most accurate. Ideal for engineering, metrology, and reverse engineering.
2. Structured Light Scanners
Projects patterns instead of lasers. Useful for capturing texture and high-detail surfaces.
3. Photogrammetry
Uses many photographs to reconstruct surfaces. Good for large objects but less accurate.
4. Long-Range Laser Scanners
Used for architecture, construction, vehicles, aircraft, and large environments.
Tangent Solutions primarily uses metrology-grade laser and structured-light scanners for engineering accuracy.
What Happens After a 3D Laser Scan?
The raw scan is just the beginning. Once captured, Tangent Solutions processes the data by:
-
Aligning scan passes
-
Cleaning noise
-
Building a watertight mesh
-
Scaling and verifying dimensional accuracy
-
Converting mesh to CAD (optional)
-
Exporting files in your chosen format
Deliverables include:
-
STL / OBJ mesh
-
STEP / IGES / XT CAD files
-
NURBS surfaces
-
2D drawings
-
Deviation analysis reports
If needed, we also provide reverse engineering, prototyping, and CAD design services.
How Long Does 3D Laser Scanning Take?
Typical project timelines:
| Project Type | Scan Time | Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Small components | 30–60 minutes | Same day to 24 hours |
| Medium mechanical parts | 1–3 hours | 1–3 days |
| Large equipment | 3–8+ hours | 2–5 days |
| Scan-to-CAD projects | Varies | 3–7+ days |
Tangent Solutions offers same-day scanning and fast turnaround for urgent engineering needs.
Why Engineers Choose Tangent Solutions
Tangent Solutions is an engineering-focused provider offering:
-
Metrology-Grade 3D Laser Scanning
-
Reverse Engineering
-
Scan-to-CAD Modeling
-
Manufacturing-Ready CAD
-
Rapid Prototyping Support
-
On-Site & Mobile Scanning Nationwide
We work with aerospace manufacturers, motorsports teams, automotive engineers, industrial plants, consumer product companies, and more.
Conclusion
3D laser scanning is transforming how engineers design, validate, and manufacture products. It delivers unmatched accuracy, speed, and efficiency — enabling companies to innovate faster and reduce costly measurement errors.
Whether you’re reverse engineering a complex part, validating manufacturing tolerances, or developing new products across industries like aerospace, motorsports, automotive, manufacturing, or defense, 3D scanning gives your engineering team a powerful advantage.
If you’re ready to integrate professional scanning into your workflow, Tangent Solutions offers industry-leading equipment, engineering expertise, and fast turnaround times. Find out more about our specific 3D scanning services to learn about the process or book your project today.