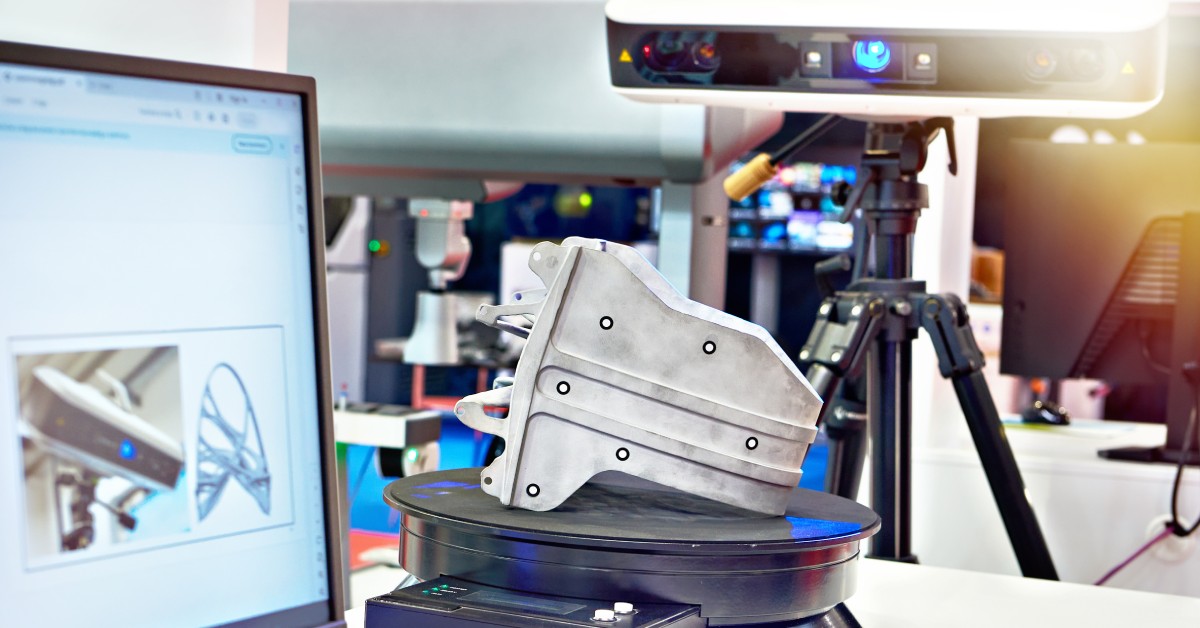
Introduction to Laser Scanning
In today’s competitive world of product development, companies need to turn ideas into reality faster and more accurately. Traditional measuring methods often struggle to capture the exact shape of complex parts. This is especially true for older components that do not have documentation or CAD models.
3D laser scanning is a great tool. It captures real-world shapes quickly and accurately in a digital format. More importantly, when you combine CAD modeling with reverse engineering skills, it creates a full process. This process turns physical parts into CAD data that is ready for production.
In this article, we will explain how 3D laser scanning works. We will show how we turn raw scan data into usable CAD files. We will also discuss why this process changes product design, reverse engineering, and manufacturing.
What Is Laser Scanning?
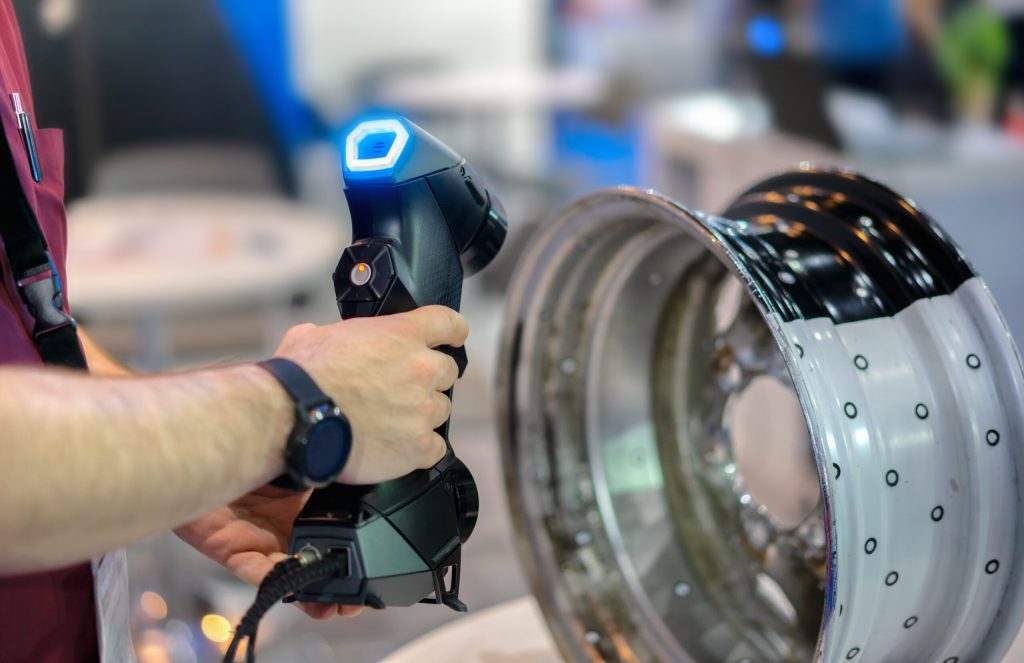
3D laser scanning is a method that captures the shape and size of objects without touching them. It creates a digital version of the object. It works by projecting laser light over the surface of an object and measuring how that light reflects back.
Specialized cameras gather this information. They measure the distance from the scanner to millions of points on the object. This creates a very detailed “point cloud.” Each point represents an exact coordinate in 3D space, capturing even subtle surface variations.
This method is dramatically faster and more precise than manual measurement. In just minutes, scanners can gather millions of data points with very high accuracy. They can do this even with complex shapes and curves.
How 3D Laser Scanning Works
3D laser scanning works mainly through triangulation. A laser shines on the object, and sensors capture the reflection. Then, software calculates the exact distances using angles.
Depending on the scanner type, data is captured in one of two ways:
- Static/Tripod Scanning: The scanner remains fixed and slowly sweeps across the object. When small tolerances are not necessary, users prefer tripod laser scanners. These scanners are ideal for large structures, buildings, and vehicles.
- Mobile/Handheld Scanning: A portable scanner is moved around the part. Ideal for small to mid-size parts, mechanical components, and field work.
Scanners also use reference targets or tracking systems to align multiple passes into a single unified 3D scan. The result is an ultra-precise digital replica of the part’s outer surface.
What You Get: Raw Scan Data
After the physical scanning session, the immediate result is a raw point cloud. This dense set of millions of XYZ points is accurate but not yet usable for design or manufacturing.
Point clouds have several challenges:
- They are extremely large files
- They contain noise and stray points
- They represent only surfaces, not solid geometry
- They are not parametric or dimension-driven
This is where reverse engineering and CAD expertise become critical.
From Scan to CAD: Reverse Engineering the Data
Turning scan data into usable CAD files is known as reverse engineering. It bridges the gap between raw geometry and fully editable design data.
Here’s the typical workflow:
- Data Cleanup
- Remove noise, misalignments, and redundant scans to create a clean, accurate point cloud.
- Mesh Generation
- Convert the point cloud into a watertight polygon mesh (STL/OBJ). This creates a continuous digital surface.
- Feature Extraction
- Use CAD tools to rebuild surfaces, sketches, and features based on the mesh.
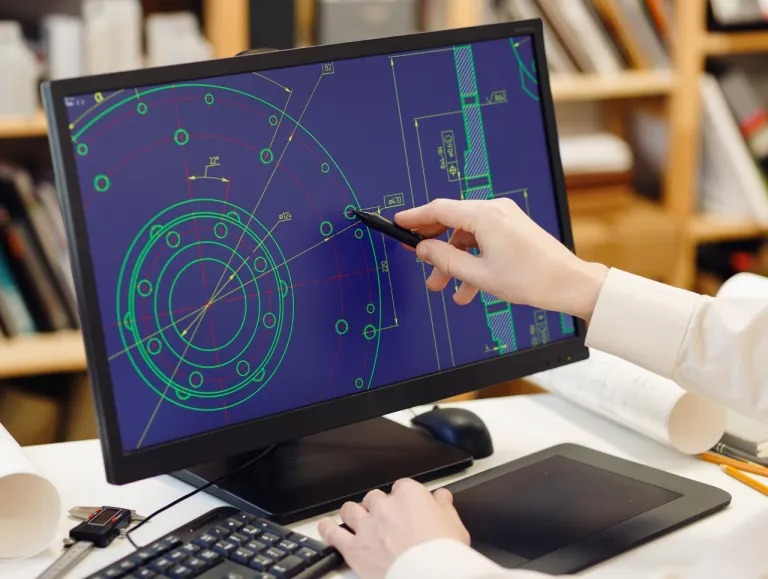
- Solid Modeling
- Make a parametric CAD model in STEP, IGES, or a native CAD format. This model should match the part’s shape. It must be easy to edit, add dimensions, and prepare for manufacturing.
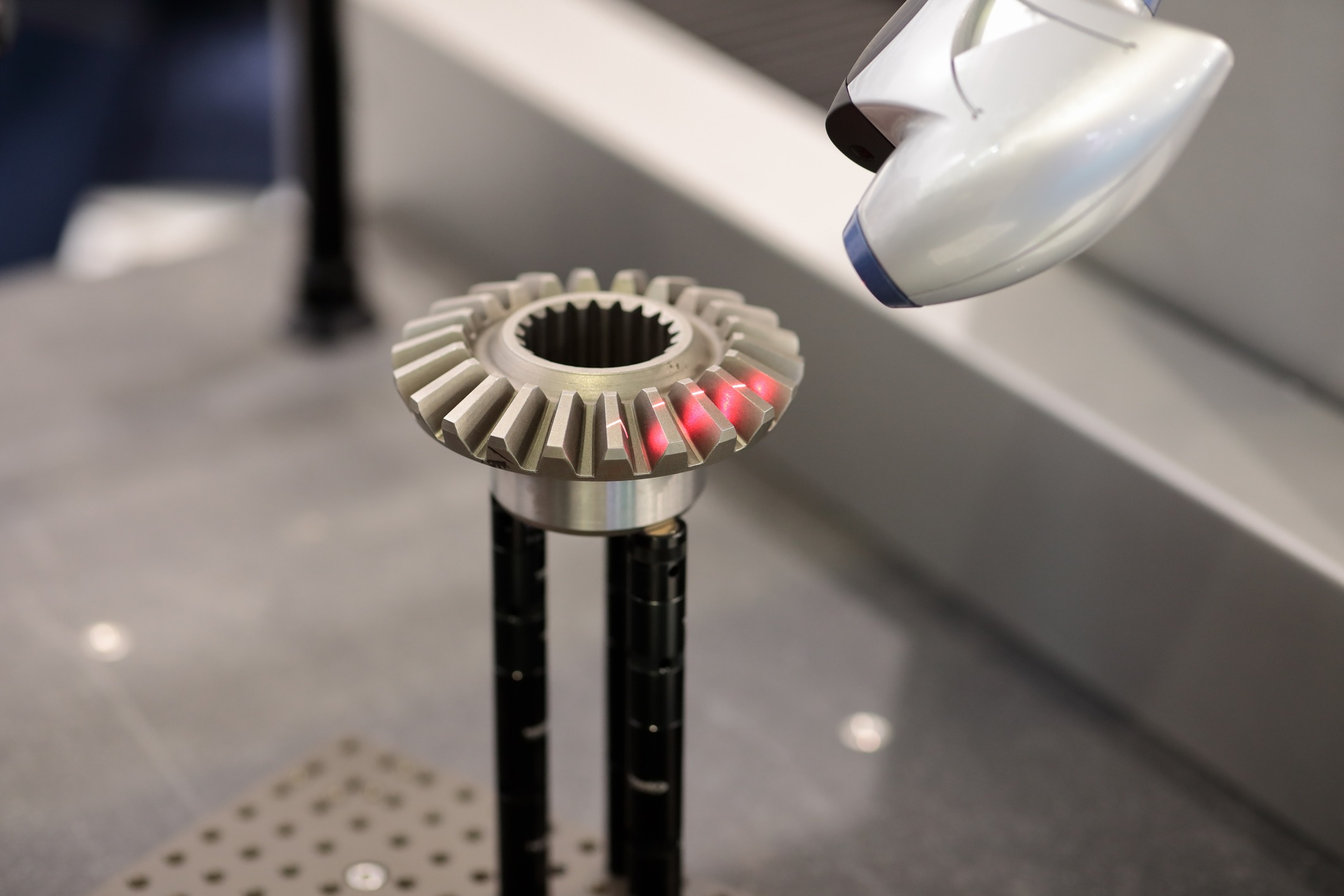
- Verification
- Compare the CAD model back to the original scan to confirm accuracy within specified tolerances.
This process demands both engineering expertise and deep knowledge of manufacturing requirements. You cannot edit or machine a mesh model by itself. Only a fully reverse–engineered CAD file lets engineers change, make, or check the part.
Why Reverse Engineered CAD Is So Valuable
Reverse engineering is not just about copying old parts. The focus is on making them easy to produce again. This process also helps improve future designs. Companies use this workflow to:
- Rebuild legacy parts that lack CAD documentation
- Create CAD for aftermarket or obsolete components
- Redesign parts for improved performance or materials
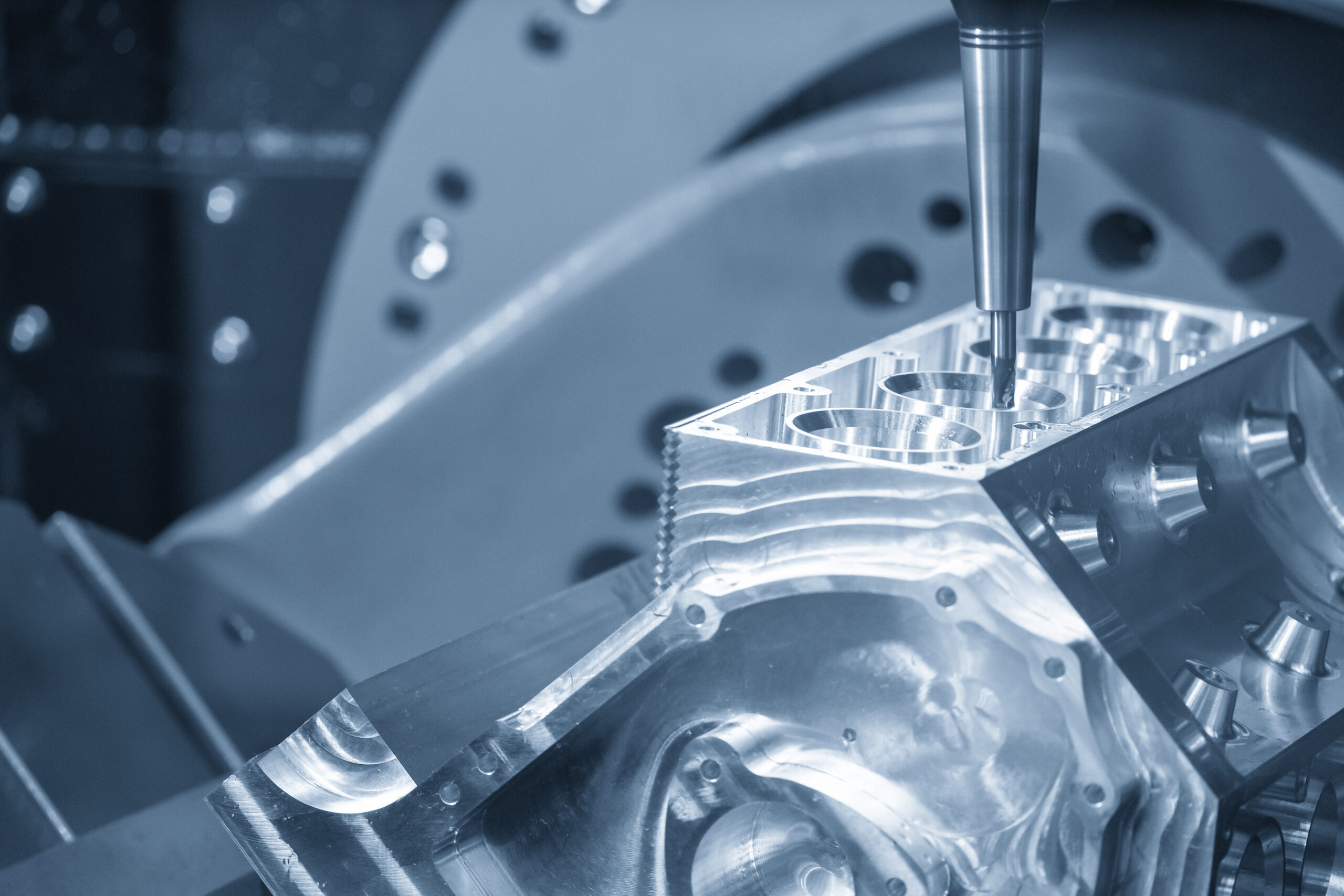
- Prepare components for CNC machining, injection molding, or 3D printing
- Generate digital twins for quality control and lifecycle tracking
For manufacturers, going from scan to CAD to production is a significant transformation. It cuts lead times and reduces costly design mistakes.
Benefits of 3D Laser Scanning for Product Design
Integrating 3D laser scanning into the design process brings major advantages:
- Speed: Capture complex shapes in minutes instead of hours of manual measurement
- Accuracy: Sub-millimeter precision reduces errors and rework
- Design freedom: Scan organic shapes and freeform surfaces impossible to measure manually
- Seamless CAD integration: Feed real-world data directly into design software
- Rapid iteration: Use scan data to prototype, test, and refine designs faster
This combination of speed and accuracy is why many companies use 3D scanning. These companies are in industries like automotive, aerospace, consumer products, and industrial equipment. They use 3D scanning more often during the development of new products.
Best Practices for Successful 3D Scanning
While 3D scanning is powerful, results depend heavily on preparation and execution. Here are key best practices Tangent Solutions follows on every project:
- Define the purpose: Know how the data will be used (inspection, CAD modeling, reverse engineering) before scanning
- Plan the scope: Decide which features and tolerances are critical to capture
- Collect more data than needed: High-resolution scans and full coverage avoid costly rescans
- Use proper surface prep: Apply temporary scan spray on shiny or transparent surfaces to ensure accurate readings
- Control alignment: Use targets or tracking systems for consistent, mergeable data
- Validate results: Compare scan and CAD alignment before sign-off
These steps ensure your scan results are accurate, complete, and ready for downstream engineering use.
The Future of 3D Laser Scanning Technology
3D scanning technology continues to advance rapidly. Today’s portable systems are faster, more accurate, and more versatile than ever — able to operate virtually anywhere. Emerging improvements include:
- Higher resolution sensors that capture ultra-fine detail
- Real-time scan alignment and tracking to speed up data collection
- Automated feature recognition to accelerate CAD conversion
- Improved integration with CAD and PLM systems for seamless workflows
These innovations are making 3D scanning easier for companies of all sizes. They help more industries use scan-based design in their operations.
How Tangent Solutions Transforms Scans Into Production-Ready CAD
Capturing data is only the beginning. The real value comes from what you can do with it.
At Tangent Solutions, our team specializes in reverse engineering scan data into fully manufacturable CAD models. We combine metrology-grade 3D scanning equipment with advanced CAD expertise to deliver:
- Clean, accurate point clouds and meshes
- Native CAD models (SolidWorks, Creo, NX, etc.) built from scan data
- Manufacturable files ready for CNC, injection molding, sheet metal, or 3D printing
- Detailed 2D drawings for production or inspection
This complete pipeline — from scanning to CAD — helps companies bring new products to market faster, replicate legacy parts, and improve existing designs with confidence.
Bring the Power of 3D Scanning to Your Next Project
3D laser scanning is reshaping how companies design, reverse engineer, and manufacture products. By combining cutting-edge scanning technology with expert CAD modeling, Tangent Solutions helps companies turn physical parts into accurate, editable digital models — ready for production.
Tangent Solutions offers professional 3D laser scanning services to help companies design, improve, and manufacture products with speed and precision. Our mobile 3D scanners capture accurate data for reverse engineering, rapid prototyping, and CAD modeling, empowering your team to innovate faster.