With 3D laser scanning technology becoming more accessible, there’s often confusion about the capabilities of 3D laser scanners and if scan to CAD conversion for file delivery is possible.
A common question we are asked by our clients is “can a 3D scanner complete scan to CAD conversion, instantly?”
It is a common misconception that a 3D laser scanner can output a 3D scan to CAD files, instantly.

In order to educate you on the file export capabilities of a 3D laser scanner, the 3D laser scanning process needs to be explained along with the differences between STL meshes and CAD files, and the process converting each.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the process of turning a 3D scan to CAD files and why STL meshes cannot be considered CAD files.
Understanding 3D Laser Scanning
3D laser scanning is a technology that captures the physical shape and dimensions of real-world objects and converts them into digital 3D representations.
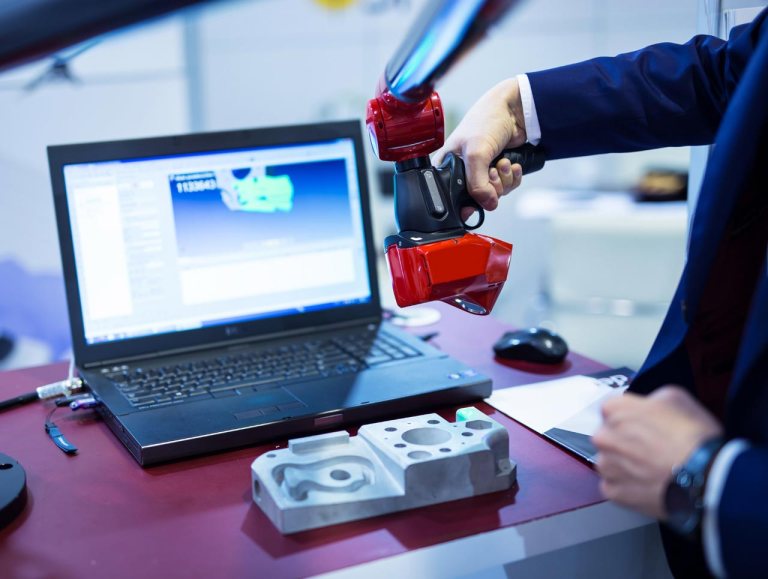
For laser scanners specifically, a handheld scanner works by emitting lasers towards a target object or and measuring the time it takes for the beams to bounce back to the scanner. This data is then used to create a point cloud, which is a collection of 3D coordinates representing the scanned surface.
While 3D laser scanners are powerful tools for capturing real-world geometry, they do not inherently generate CAD files. The initial point cloud is a mesh, a collection of surfaces, distances, angles, and faces represented into a shape.
What is a CAD File?
A CAD file, short for Computer-Aided Design file, is a digital representation of a 2D or 3D object created using specialized CAD software.

CAD files are used extensively in engineering, architecture, product design, and manufacturing to create precise, detailed 3D models.
These files typically contain information about the object’s geometry, dimensions, and other properties. CAD files come in various formats, such as STEP, XT, and IGES, each designed for specific applications and compatibility with various CAD software.
What is a Mesh File?
A mesh file, in the context of 3D modeling, is a collection of vertices, edges, and faces, meeting together to create a representation of a 3D object’s surface or geometry.
The most common file formats are STL and OBJ files. During the 3D laser scanning process, the immediate export after clean up is an STL file.
For projects that require mesh files, generally STL files are delivered. STL, or Stereolithography, is a common file format used for 3D printing and 3D visualization.
This simplicity makes STL files suitable for 3D printing and rapid prototyping but proceed with caution because of the lack of complexity in the files.
STL Mesh vs. CAD Files
STL files do not contain information about the object’s parametric design or original intent. Instead, they focus solely on the surface geometry. This is why STL files are not justified for use in manufacturing, simulation, or other engineering applications.
However, an STL mesh is a great representation of the object, when collected with the purpose of converting a 3D scan to CAD file.
Mesh files have their place in engineering but CAD files are essential to manufacturing, simulations, and more.
In contrast, CAD files are highly detailed and contain comprehensive information about an object’s design. CAD files store parametric data, which means the geometry is defined by mathematical equations and constraints, allowing for easy modifications and precise measurements.
These files maintain the original intent of the design, making them suitable for complex engineering and design tasks.
3D Scan to CAD Conversion
Given that 3D laser scanners produce point clouds and STL mesh files, it is necessary to convert this data into a usable CAD format. This process is known as 3D scan to CAD conversion and involves several steps
- Mesh Cleanup
The initial mesh obtained from a laser scanner may have imperfections, holes, or unnecessary details. Scan technicians use native software to clean up the mesh, removing any unwanted data and ensuring it represents the object accurately. - Surface Reconstruction
Once the mesh is cleaned up, the next step is to reconstruct the surfaces of the object. Various algorithms and software can analyze the mesh and create a smooth, parametric representation that closely resembles the scanned object. - Parametric Modeling
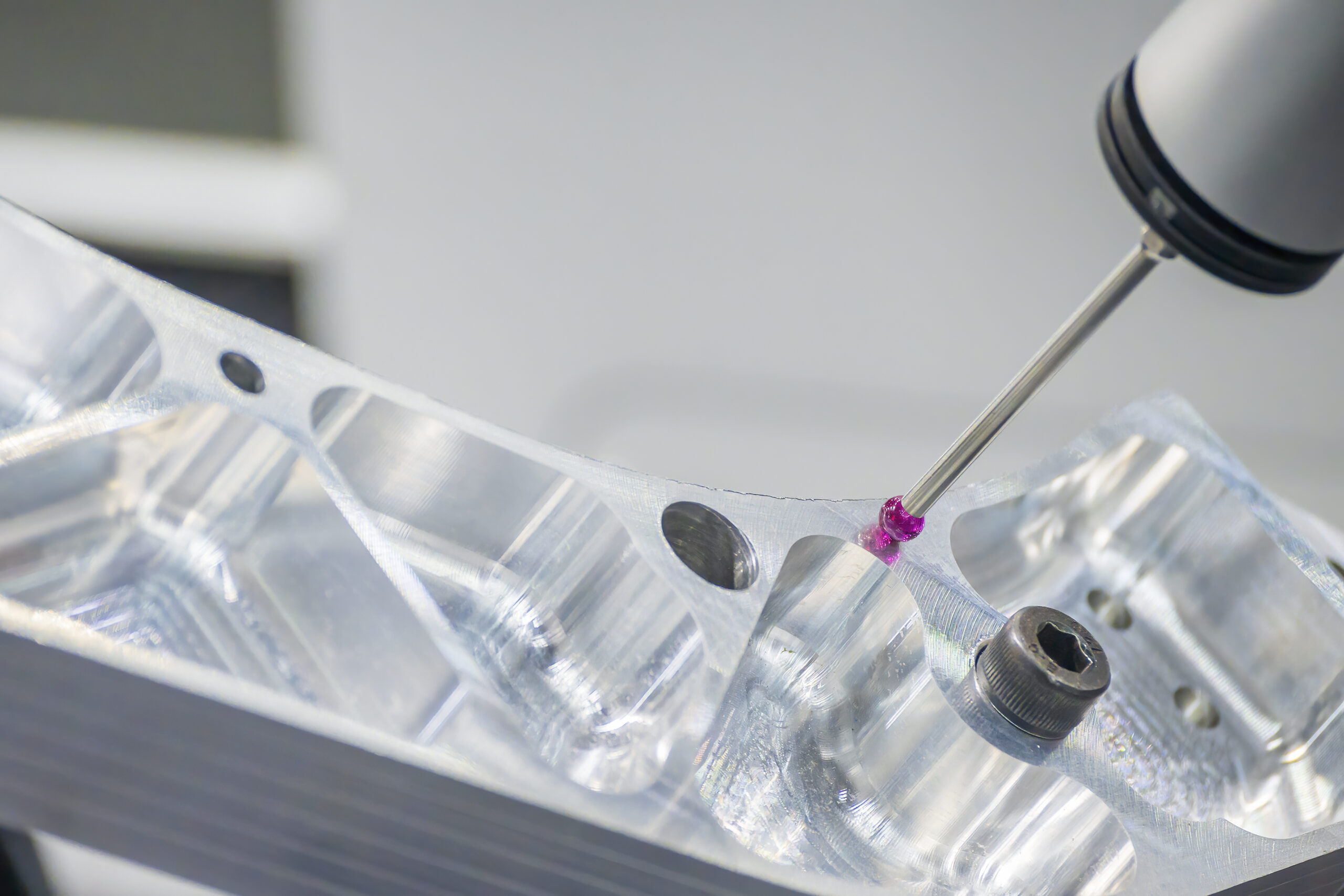
CAD professionals then use this reconstructed surface as a reference to create a parametric CAD model. They define features, dimensions, and constraints to recreate the object’s original design intent. - Quality Control
After the parametric model is created, it undergoes thorough quality control to ensure it matches the scanned object’s specifications and meets design requirements. The original mesh will be imposed on top of the CAD file to show its accuracy to scan data. - Export to CAD Format
The final step involves exporting the parametric CAD model into a standard CAD file format like STEP or IGES. This format preserves all the design information, making it suitable for further engineering and design work.
Why STL Mesh Files Are Not CAD Files
Now that we understand the process of 3D scan CAD conversion, it becomes evident why STL mesh files cannot be considered CAD files. To review, here are 4 topics of why STL files cannot be used for complex engineering projects:
- Lack of Parametric Data
STL mesh files represent the geometry of an object in a mesh structure but do not contain any parametric data or information about the object’s design intent. CAD files, on the other hand, are defined by mathematical equations and constraints, enabling precise control over the design. - Limited Usability
While STL files are excellent for 3D printing and visualizations, they lack the versatility required for engineering and design tasks. CAD files are the preferred choice when it comes to making modifications, conducting simulations, and performing complex analyses. - Loss of Detail
STL files often simplify complex geometry by approximating it with triangular facets. This simplification can result in a loss of detail and accuracy, which is unacceptable in many engineering and design scenarios. - Incompatibility with CAD Software
Most CAD software packages do not directly accept STL files for editing or further design work. Converting a mesh to a CAD format is necessary to leverage the full capabilities of CAD software.
Scan to CAD Conversion- Where Each File Is Used
To better understand the applications of STL mesh files and CAD files, let’s explore where each type finds its primary use:
STL Mesh Files
- 3D Printing
STL files are the standard format for 3D printing. They define the outer surface of an object, making them ideal for creating physical prototypes. - Visualizations and Rendering
STL files are suitable for 3D visualization and rendering applications, where the emphasis is on the object’s visual representation. - Rapid Prototyping
Engineers and designers use STL files to quickly produce prototypes of their designs for testing and validation. If functionality versus presentation is of concern, then an STL would not be the key format needed.
CAD Files
- Engineering Design
CAD files are the backbone of engineering and design work. Engineers and designers rely on CAD files to create detailed and accurate models of products, buildings, and components. - Manufacturing
CAD files are used in manufacturing processes, including CNC machining, injection molding, and sheet metal fabrication, to produce physical parts and products. - Simulation and Analysis
CAD files provide the necessary information for running simulations and analyses, such as finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD), to evaluate product performance. - Documentation
CAD files are crucial for creating comprehensive design documentation, including assembly instructions, technical drawings, and bills of materials.
Does a 3D Laser Scanner Instantly Complete Scan to CAD Conversion?
Now we have explored the differences between STL mesh files and CAD files.
With understanding the process of mesh to CAD conversion, we can answer the question: “can a 3D laser scanner convert a 3D scan to CAD, instantly?”
The short answer is no, a 3D laser scanner cannot directly create a CAD file.
While 3D laser scanners excel at capturing the physical shape and dimensions of objects or environments, the data they produce is typically in the form of point clouds or mesh files.
These files lack the parametric information and design intent necessary for CAD work.
However, with the use of specialized software and the expertise of CAD professionals, it is possible to convert the data from a 3D scan to CAD files. This process involves cleaning up the mesh, reconstructing surfaces, and creating a parametric CAD model that accurately represents the scanned object.
Where to Next
3D laser scanners are valuable tools for capturing real-world geometry, but they do not directly create CAD files.
The data they produce, in the form of point clouds or STL mesh files, lacks the precision and design intent required for engineering and design work.
CAD files, on the other hand, are the foundation of modern engineering and design processes, containing detailed parametric information about an object’s geometry.
Mesh to CAD conversion is the key to bridging the gap between 3D laser scanning and CAD design. This process involves cleaning up the mesh, reconstructing surfaces, and creating a parametric CAD model that preserves the original design intent.
While it requires expertise and specialized software, it enables engineers and designers to leverage the full capabilities of CAD for precise modeling, analysis, and manufacturing.
The above information will help you understand the difference between meshes and CAD. All you will need to do is choose which type of file best suits your needs.
Understanding the distinction between STL mesh files and CAD files is essential for professionals working in fields that rely on accurate 3D representations. By recognizing the strengths and limitations of each file type, you can make informed decisions about when and how to use 3D laser scanning and CAD modeling in your projects, ultimately leading to more efficient and successful outcomes.