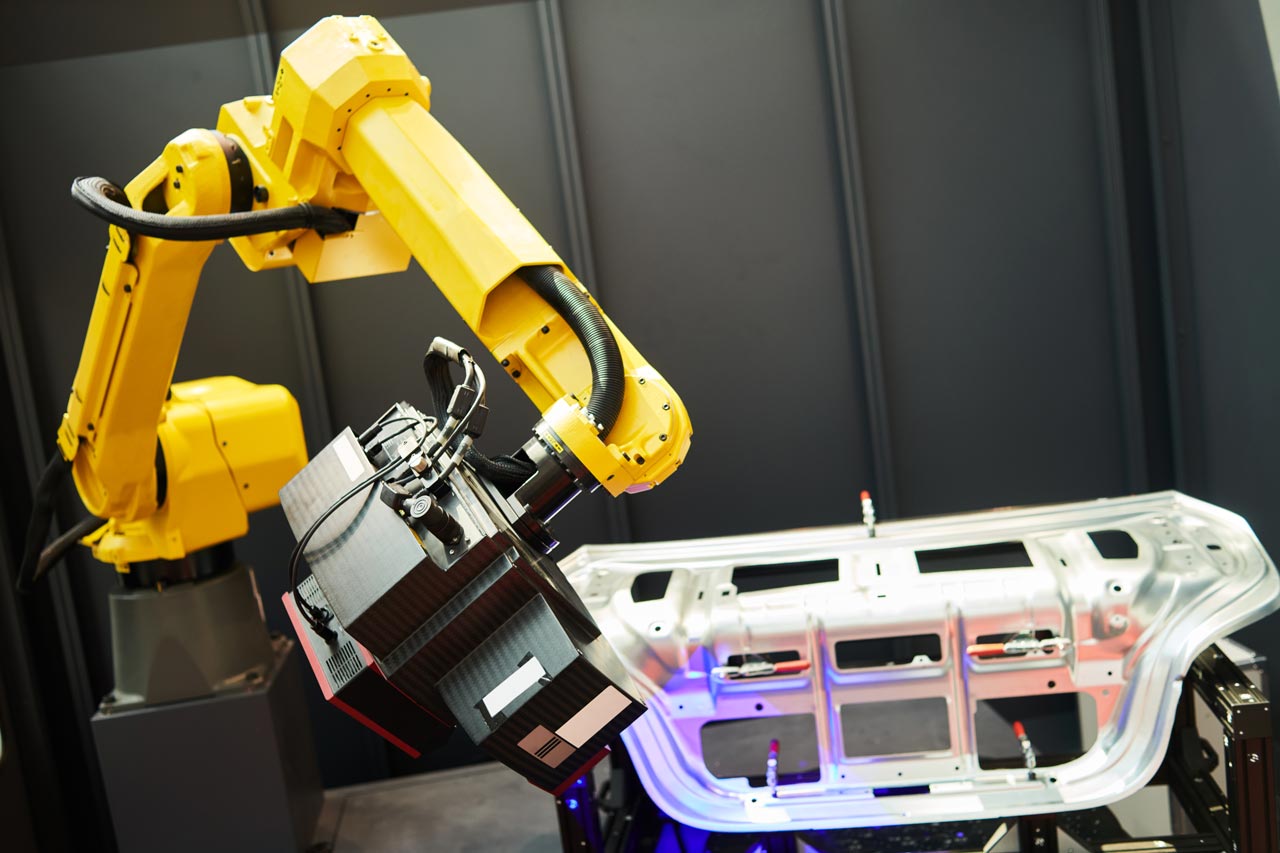
Are you looking to reverse engineer a project? Whether you don’t have a usable 3D model or want to make modifications to an existing model, you will need to perform the reverse engineering process.
Gone are the days of using handheld calipers. Most companies turn to 3D scanning services in order to reverse engineer a product, producing an ultra-precise digital model. 
There are a few different ways to create a 3D model of an object but the most common method is to use a 3D scanner. A 3D laser scanner is a device that captures the shape and appearance of an object in digital form. 3D scanners come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and they can be used for a variety of different purposes.
3D scanners have gained popularity as an indispensable tool for manufacturing and prototyping products. Finding the best 3D scanner for reverse engineering allows you to replicate existing items to gain a better understanding of its design.
Moreover, reverse engineering has a lot of exciting potential for manufacturing companies. With all the 3D scanner options, how can you know which ones to choose? Here are some topics to consider when looking for the best 3d scanner for reverse engineering.
Types of 3D Scanners
There are several different types of 3D scanners on the market today, each with its own set of features and capabilities. The type of scanner you choose will depend on your specific needs and budget.
There are three main types of 3D laser scanners:
- Structured Light Scanners: Use a pattern of light to scan an object and create a 3D model.
- Blue Light Laser Scanner: Use a laser beam to scan an object and create a 3D model.
- CT Scanners: Use X-rays to scan an object and create a 3D model.
Now, let’s have a look at what the best 3d scanner for reverse engineering purposes is and how it can be used.
What Is Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering is the process of working backward from a finished object to create a new item that matches the original object. It’s also often used to gain a better understanding of how something works.
Traditional reverse engineering involves using an existing machine or object as the design plan for a new object. The process often involves taking an item apart to see how it’s assembled and what it is made up of. Lots of manual labor is needed with tools and calipers.
However, new 3D laser scanners have made reverse engineering easier than ever. The best 3D scanner for reverse engineering will create accurate 3D models of items without the need for trial and error using CAD software.
How Can 3D Scanners Be Used for Reverse Engineering?
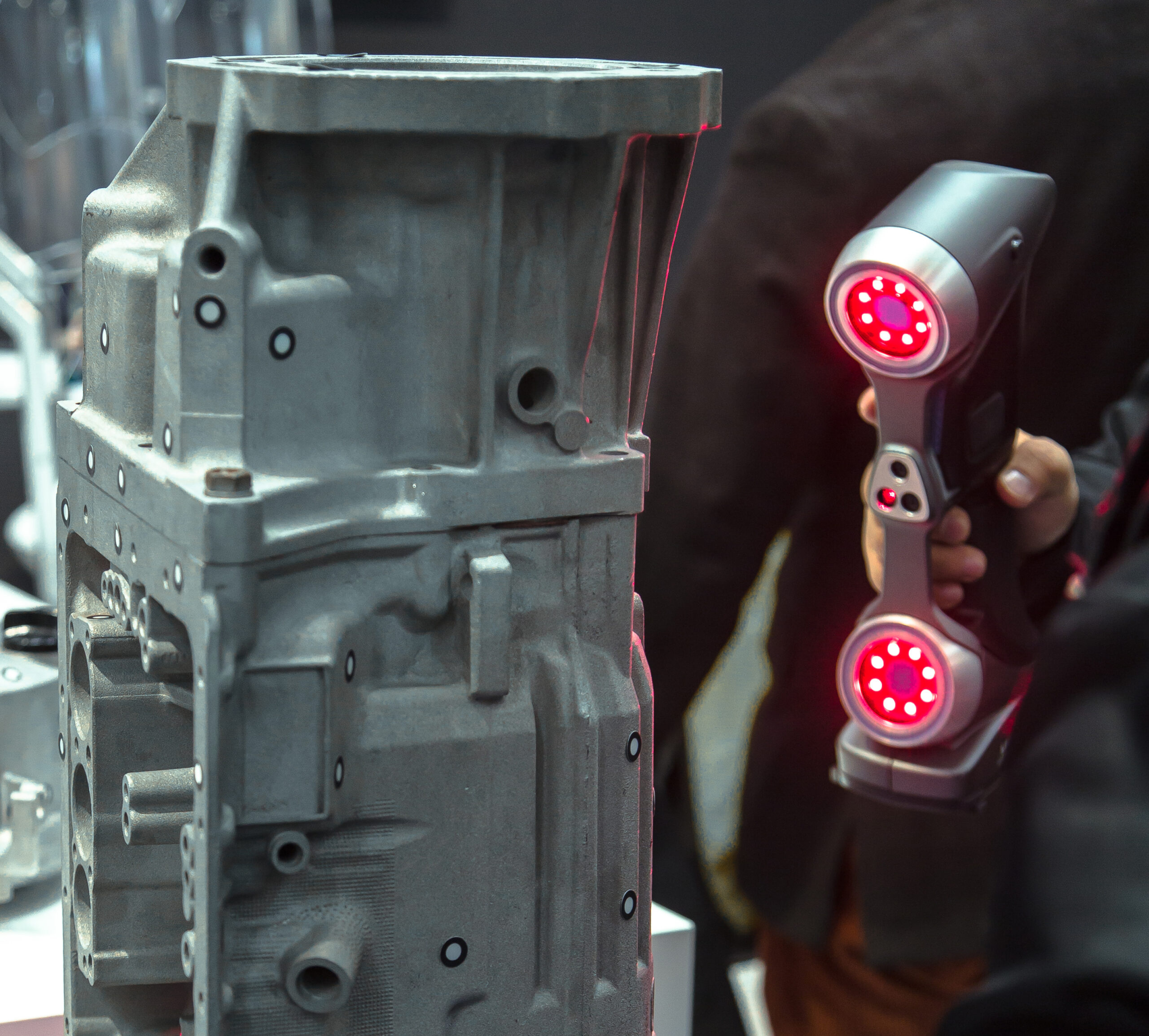
3D laser scanners create 3D models of the objects they scan. When it comes to reverse engineering components, this is a very useful ability. A series of lasers or light are passed over an existing project to gather data of its size, shape, and distance features.

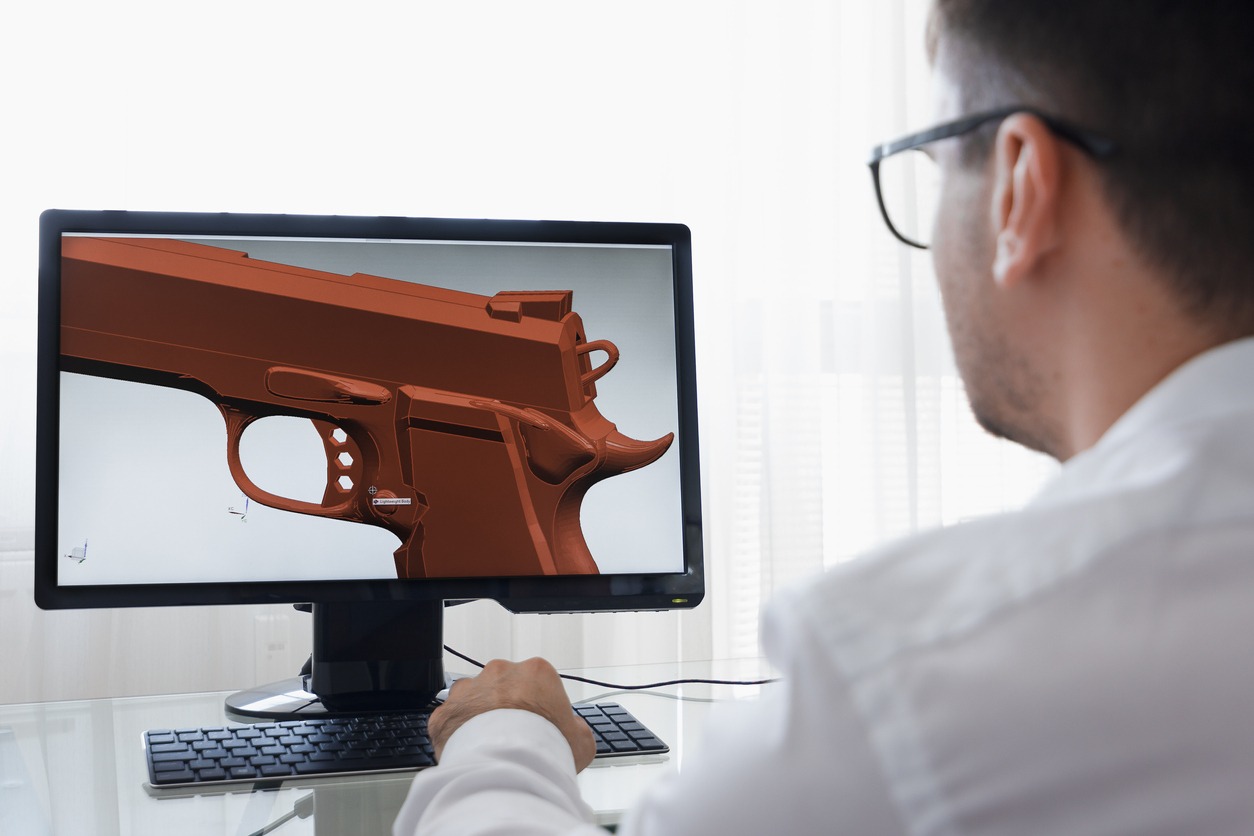
Once the scanner has created a model, engineering teams can view the results instantly on a computer screen. From there, data is categorized with planes, dimensions, and sketches to be exported and redrawn in CAD software; creating CAD, manufacturable files. This is essentially the reverse engineering process.
The 3D mesh model has millions of points that capture an object’s shape and size. 3D scanners can be used on items in a wide variety of sizes, and once they are reverse engineered as 3D models, there are endless ways to use that data for the production, research, and refinement of your next product.
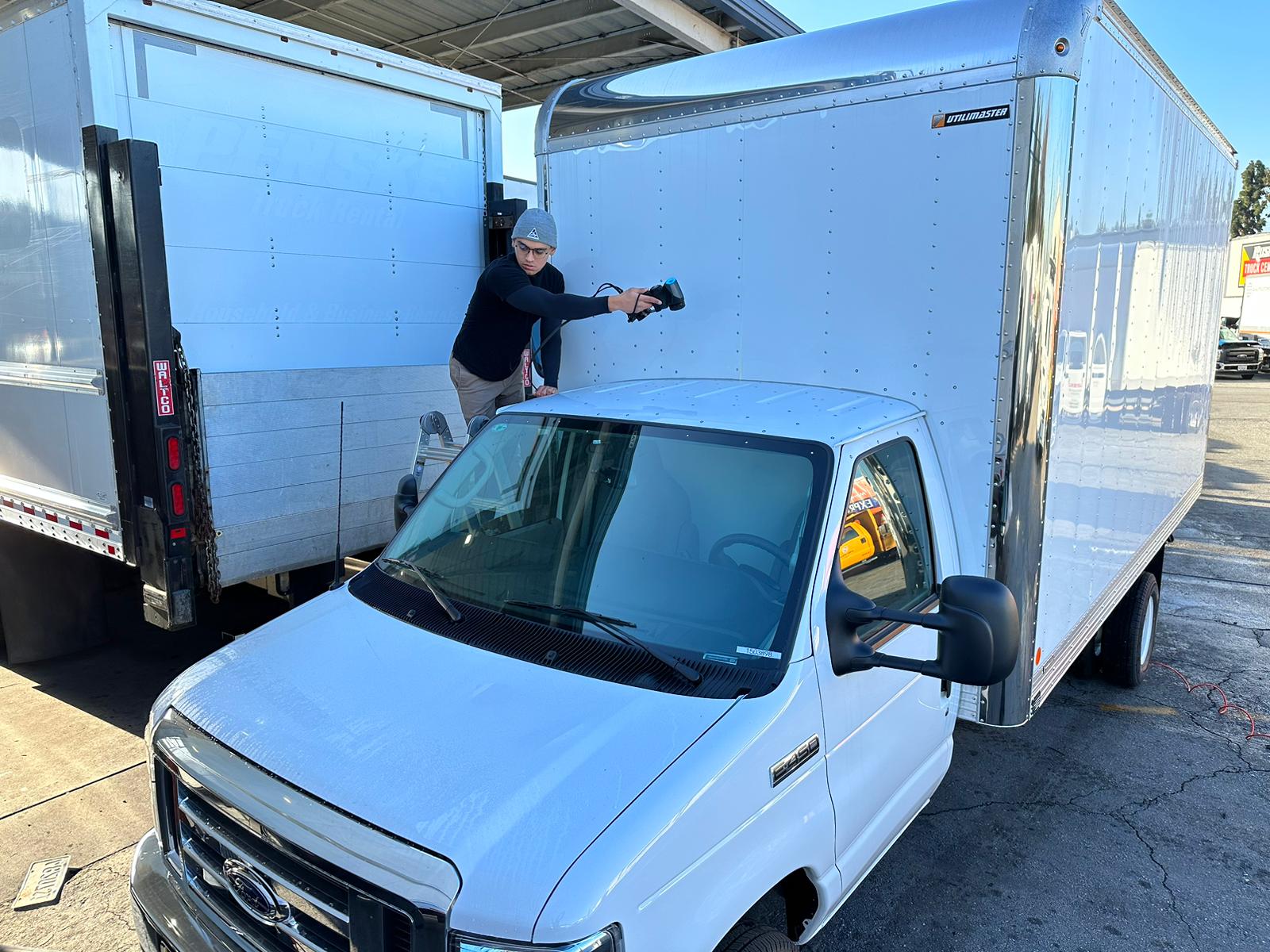
What is truly amazing is the latest 3D scanning technology has no size limitations, allowing large and remote projects to be scanned at any location.
What Is the 3D Scan Reverse Engineering Process?
Using a 3D laser scanner is more efficient and more accurate than traditional reverse engineering practices.
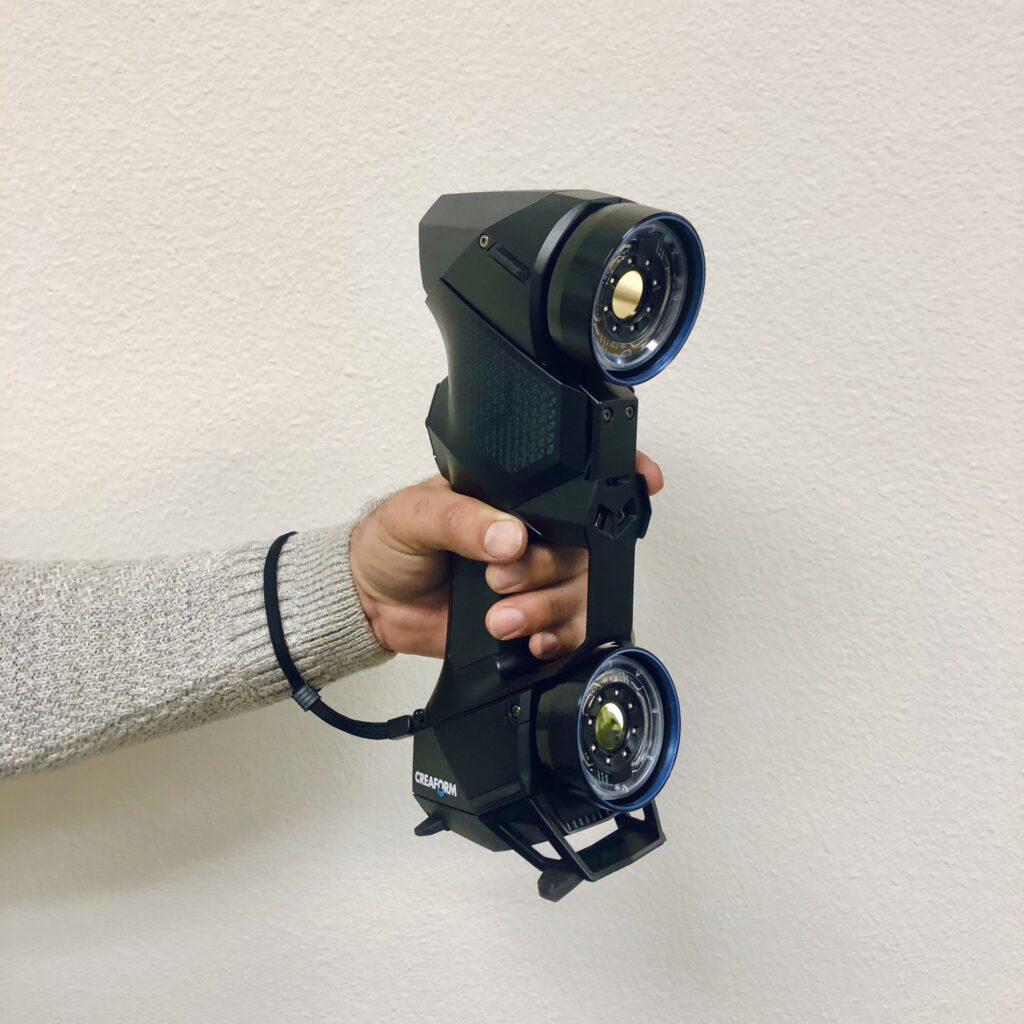
Now depending upon the 3D laser scanner you purchase, there may be some extra steps in the scanning process. Currently we have one of the best 3D scanner for reverse engineering purposes on the market, a Creaform HandyScan Black Elite, with precision of up to 0.02mm. 
The scanning platform our company uses is not affected by light or reflectivity. If using a different scanner, you may need to cover any transparent or reflective parts of your item with something matte, like a CAD/CAM spray. This step is important because it ensures accurate results and prevents the scanning lasers from reflecting back or away from the scanner.
After this, you can use your scanner to acquire data points in the shape of the item you’re scanning. In our platform, this is done by placing small targets throughout the scan area. By way of triangulation, the lasers will map out millions of points onto a digital mesh.
After 3D laser scanning is complete, the technician will refine 3D scan data by cleaning up any erroneous data and validating all components were recorded thoroughly. This ensures it accurately reflects every detail of your prototype. If you missed something, simply don’t move the object and turn the scanner back on to fill in details until you’re left with a complete and accurate scan.
When post processing is completed, you can export your accurate scan to reverse engineer in your preferred CAD software.
Which 3D Scanners are Best for Reverse Engineering?
There are several types of 3D scanners available but there are few that are the best 3D scanner for reverse engineering.
Laser-based 3D scanners offer the most reliability and widely used options. This scanning platform uses lasers to capture millions of points on a given object that can be used to make accurate measurements. Many of them are portable, as well, and this one of the key advantages when considering the best 3D scanner for reverse engineering. 
Other 3D laser scanners use structured light to measure objects. They project a grid of lights onto the object being scanned, and the grid allows the scanner to measure distances. This option may require more preparation and specific lighting. They are also not as precise in measurement as laser scanners.
Wrapping Up
There are many types of 3D scanners used for reverse engineering. The most common are laser scanners, CT scanners, and white light scanners. Each type of scanner has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Laser scanners are the most accurate but can be expensive. CT scanners are less accurate but are less expensive and can be used on a variety of materials. White light scanners are the least accurate but are the most affordable. Choosing the best 3D scanner for reverse engineering will all depend upon your project goals.